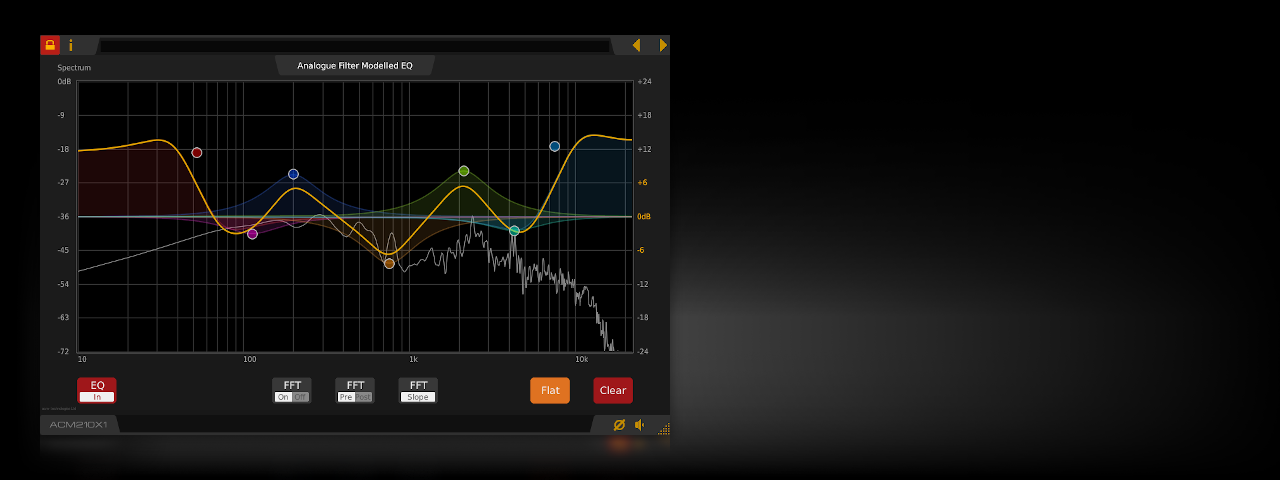
De-Cramped Analogue Modelled Filters:
At commonly used sample rates such as 44100Hz and 48000Hz, conventional digital EQs can cause frequency response cramping as the filter frequency approaches its upper limit. Conventional solutions such as oversampling can be CPU intensive, introducing other artefacts and additional latency. The ACM210X1 uses innovative analogue filter modelling technology to provide a zero latency de-cramped response, accurately replicating that of an equivalent analogue filter without requiring oversampling.
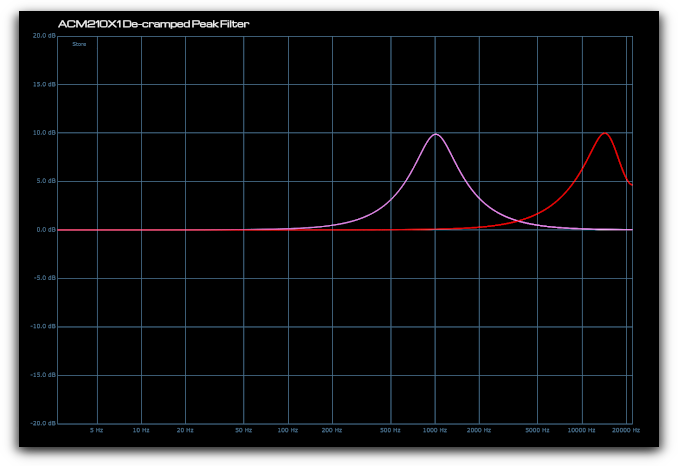
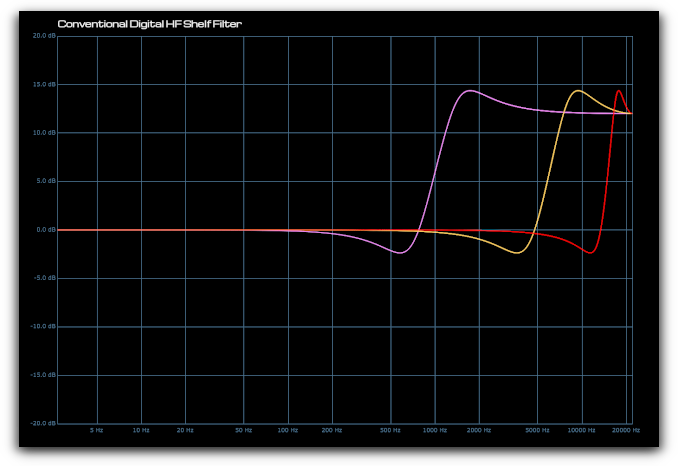
The cramping effect of a conventional EQ can clearly be seen below as the filter frequency is increased (yellow and red traces). In this instance the shelf slope becomes significantly steeper and the resonant peak becomes narrowed.
At commonly used sample rates such as 44100Hz and 48000Hz, conventional digital EQs can cause frequency response cramping as the filter frequency approaches its upper limit. Conventional solutions such as oversampling can be CPU intensive, introducing other artefacts and additional latency. The ACM210X1 uses innovative analogue filter modelling technology to provide a zero latency de-cramped response, accurately replicating that of an equivalent analogue filter without requiring oversampling.
ACM210X1 De-Cramped HF Shelving Filter
ACM210X1 De-Cramped Peak Filter
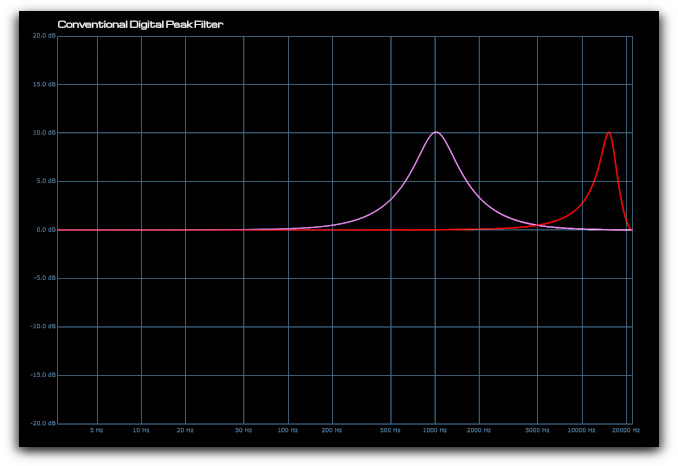
The cramping effect of a conventional EQ can clearly be seen below as the filter frequency is increased (yellow and red traces). In this instance the shelf slope becomes significantly steeper and the resonant peak becomes narrowed.
Conventional Digital HF Shelving Filter
Conventional Digital Peak Filter
System Requirements - Windows
- 64bit Windows 7 or newer.
- Graphics adapter / drivers with support for OpenGL 3.x or later.
- A compatible host application.
- Linux x86-64/AMD64 64bit e.g. Ubuntu 20.04 LTS or newer.
- Graphics adapter / drivers with support for OpenGL 3.x or later.
- A compatible host application.
- VST, VST3, AAX and CLAP compatible.
- Mono or stereo operation.
- Interpolated parameters for smooth changes with no 'zipper' noise.
- -18dBFS reference level for 0dBu.
- Equalizer:
- Number of filter bands: 10.
- Filter Q (peak filters): 0.3 to 5.0
- Filter Q (shelf / low and high-pass): 0.7 to 1.4
- Maximum boost or cut: 18dB.
- Filter types:
- High-pass: 2-pole with adjustable resonance.
- Low-pass: 2-pole with adjustable resonance.
- Band-pass: Unity gain band-pass with adjustable Q.
- HF Shelf: High frequency shelf with adjustable resonance.
- LF Shelf: Low frequency shelf with adjustable resonance.
- Peak dB / 2: Peak filter with Q determined using frequency points at which the filter gain in dB is half that of the peak. The filter provides symmetrical boost and cut responses.
- Peak -3dB: Peak filter with Q determined using frequency points at which the filter response is 3dB below that of the peak. The filter provides symmetrical boost and cut responses.
- Peak +3dB: Peak filter with Q is determined using frequency points at which the filter response is 3dB above unity (0dB) for boost, or 3dB below unity for cut. The filter provides symmetrical boost and cut responses.
- Asymmetric: Peak filter with Q determined using frequency points at which the filter response is 3dB below the peak for boost or 3dB below unity (0dB) for cut. The filter provides asymmetrical boost / cut responses in which the cut is much narrower than the boost, for the same Q setting.
- Inverse Asymmetric: Peak filter with Q determined using frequency points at which the filter response is 3dB above unity (0dB) for boost or 3dB below the peak for cut. The filter provides asymmetrical boost / cut responses in which the boost is much narrower than the cut, for the same Q setting.
- Internal processing: 64Bit floating point.
- Algorithm: Analogue filter modelling coefficient generator provides filter responses which closely model analogue equivalents, without requiring high sample rates or internal upsampling.
- FFT Spectrum analyser:
- Algorithm: Windowed Fast Fourier Transform.
- FFT Window function: Blackman - Harris.
- FFT Resolution: 1024 Frequency bins covering 0 to Fs interpolated to 4096 bins during the FFT process, where Fs is the sample rate.
- FFT Latency: 1024 samples.
- FFT Slope:
- 3dB per octave (slope switch enabled).
- Flat (slope switch disabled).
- FFT Source: Pre or post EQ, average of left and right stereo channels.
- Polarity invert switch.
- Output level trim: +/-6dB
 ACM210X1 Graphical EQ for Windows & Linux - Technical Specification
ACM210X1 Graphical EQ for Windows & Linux - Technical Specification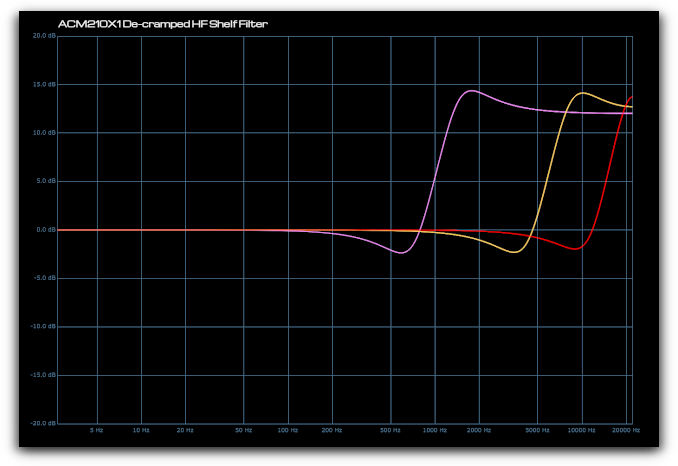
 Top
Top 
